103855
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

小剂量左西孟旦 (Levosimendan) 对中国老年脓血症患者死亡率和器官功能的影响
Authors Wang X, Li S
Received 7 March 2017
Accepted for publication 18 April 2017
Published 29 May 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 917—921
DOI http://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S136355
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Zhi-Ying Wu
Aim: As a primary cause of death not only in Western countries but also in
the People’s Republic of China, sepsis is diagnosed as abnormal organ functions as a
result of a disordered response to a severe infection. This study was designed
to assess the effect of small-dose levosimendan without a loading dose on
mortality rates and organ functions in Chinese elderly patients with sepsis.
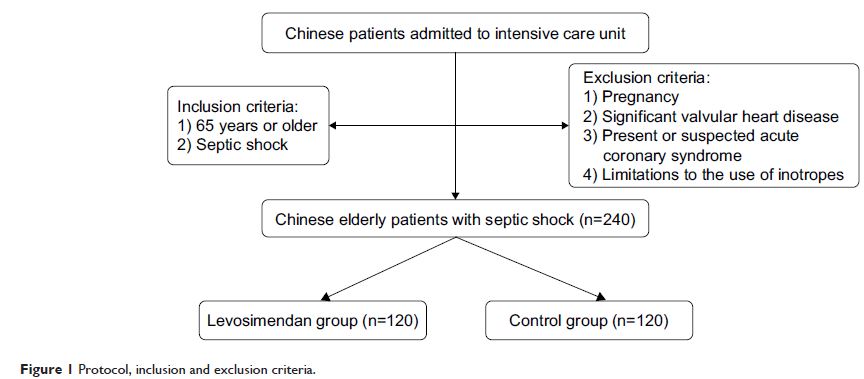
Methods: Following a prospective, randomized, and
double-blinded design, 240 Chinese elderly patients with sepsis shock were
admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). All patients were randomly and
evenly assigned into a levosimendan group (number of patients =120) and a
control group (number of patients =120). The control group underwent standard
care, and the levosimendan group was administered levosimendan in addition to
standard care.
Results: All participants, comprising 134 males (55.8%) and 106
females (44.2%), were 70 (67–73) years old. Baseline characteristics,
preexisting illnesses, initial infections, organ failures, and additional
agents and therapies showed no significant difference between the two groups (P >0.05 for all). There were no
significant differences in mortality rates at 28 days, at ICU discharge, and at
hospital discharge between the two groups (P >0.05 for all).
The number of days of ICU and hospital stay in the levosimendan group was
significantly less than for those in the control group (P <0.05 for all). Mean daily
total sequential organ failure assessment score and all organ scores except the
cardiovascular scores showed no significant difference between the two groups (P >0.05 for all). Cardiovascular
scores in the levosimendan group were significantly higher than those in the
control group (P <0.05 for all).
Conclusion: Small-dose levosimendan could not reduce the mortality
rates or enhance the respiratory, liver, renal, and coagulation functions, but
could shorten the days of ICU and hospital stay, and improve the cardiovascular
function, which suggests that small-dose levosimendan is valuable for Chinese
elderly patients with sepsis.
Keywords: Chinese
elderly, levosimendan, mortality rate, organ function, sepsis, small-dose