103855
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

亲嗜性病毒整合位点 1 的过表达是肺鳞状细胞癌的一个预后因素
Authors Xu X, Liu S, Ji X
Received 14 January 2017
Accepted for publication 17 March 2017
Published 26 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2739—2744
DOI http://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S132410
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
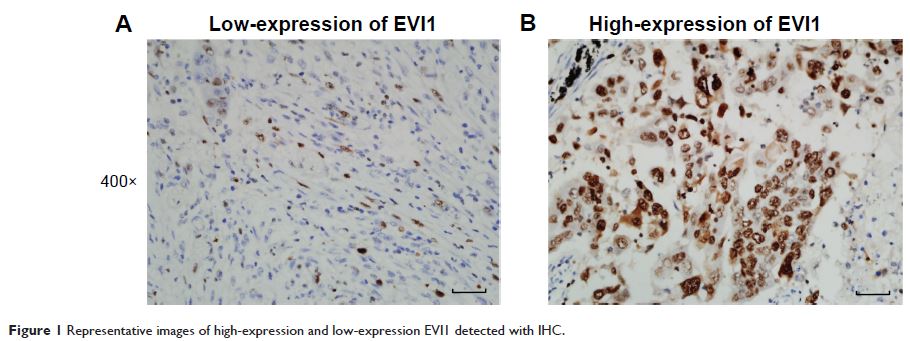
Aim: To explore the expression and clinical significance of ecotropic viral
integration site-1 (EVI1) of lung squamous cell cancer (SCC).
Methods: The expression of EVI1 in SCC was detected by
immunohistochemistry and the validation cohort was divided into EVI1
high-expression group and low-expression group according to the cutoff of
immunohistochemical score. The correlations between EVI1 expression and the
clinicopathological factors were analyzed by χ 2 test. The relation between EVI1
expression and overall survival rate was evaluated by univariate analysis with
Kaplan–Meier method. The independent prognostic factor was identified by
multivariate analysis with Cox regression model.
Results: In this study, the EVI1 high-expression percentage was
32.32% (53/164). EVI1 high expression was significantly associated with a
poorer overall 5-year survival rate of SCC (P =0.021). Moreover,
EVI1 high expression was identified as an independent prognostic factor of SCC,
predicting the unfavorable prognosis (P =0.013).
Conclusion: High expression of EVI1 was significantly associated
with a poorer prognosis and it was identified as an independent prognostic
factor of SCC.
Keywords: ecotropic viral integration site-1,
lung squamous cell cancer, biomarker, prognosis, immunohistochemistry, overall
survival rate