103855
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肿瘤坏死因子 α 顺利获得 p38 MAPK 激活途径调节大鼠脊髓背角神经元中的钠激活钾离子通道 SLICK
Authors Wang K, Wang F, Bao J, Xie Z, Chen L, Zhou B, Xie X, Wu X
Received 11 January 2017
Accepted for publication 24 April 2017
Published 25 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1265—1271
DOI http://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S132185
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
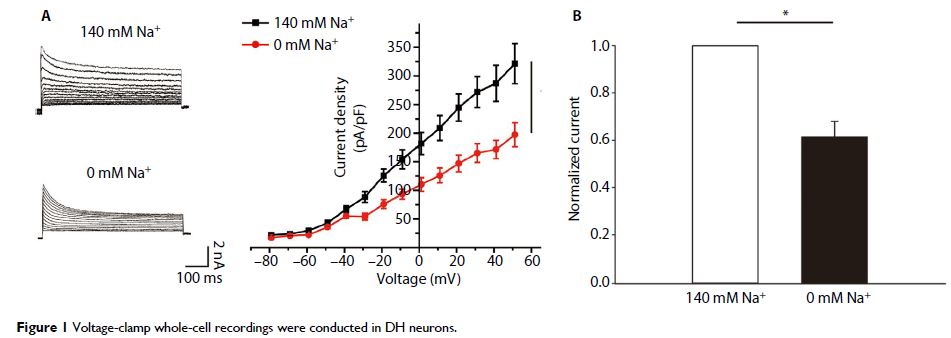
Abstract: The dorsal horn (DH) of the spinal cord is the integrative center that
processes and transmits pain sensation. Abnormal changes in ion channel
expression can enhance the excitability of pain-related DH neurons.
Sodium-activated potassium (KNa) channels are
highly expressed particularly in the central nervous system; however,
information about whether rat DH neurons express the SLICK channel protein is
lacking, and the direct effects on SLICK in response to inflammation and the
potential signaling pathway mediating such effects are yet to be elucidated.
Here, using cultured DH neurons, we have shown that tumor necrosis factor-α
inhibits the total outward potassium current IK and the KNa current predominantly as well as
induces a progressive loss of firing accommodation. However, we found that this
change in channel activity is offset by the p38 inhibitor SB202190, thereby
suggesting the modulation of SLICK channel activity via the p38 MAPK pathway.
Furthermore, we have demonstrated that the tumor necrosis factor-α modulation
of KNa channels
does not occur at the level of SLICK channel gating but arises from possible
posttranslational modification.
Keywords: p38 MAPK, SLICK channel, neuropathic
pain, dorsal horn, TNF-α