103855
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Bisdemhoxcurcumin 与 α-PD-L1 抗体结合可增强膀胱癌的免疫反应
Authors Shao Y, Zhu W, Da J, Xu M, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang Z
Received 19 December 2016
Accepted for publication 13 April 2017
Published 22 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2675—2683
DOI http://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S130653
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Abstract: Curcumin was recently discovered to strengthen immune response through
multiple mechanisms. Cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells play a critical role in modulating
anticancer immune response, but is severely restricted by T-cell exhaustion.
Bladder carcinomas express PD-L1 and can abrogate CD8+ T-cell
response. Thus, we hypothesized that bisdemethoxycurcumin, a natural dimethoxy
derivative of curcumin, may provide a favorable environment for T-cell response
against bladder cancer when used in combination with α-PD-L1 antibody.
Immunocompetent C56BL/6 mouse models bearing subcutaneous or lung metastasized
MB79 bladder cancer were established to validate this conjecture. We found that
bisdemethoxycurcumin significantly increased intratumoral CD8+ T-cell
infiltration, elevated the level of IFN-γ in the blood, and decreased the
number of intratumoral myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Furthermore, α-PD-L1
antibody protected these amplified CD8+ T-cells from exhaustion, and therefore
facilitated the secretion of IFN-γ, granzyme B, and perforin through these CD8+ T-cells.
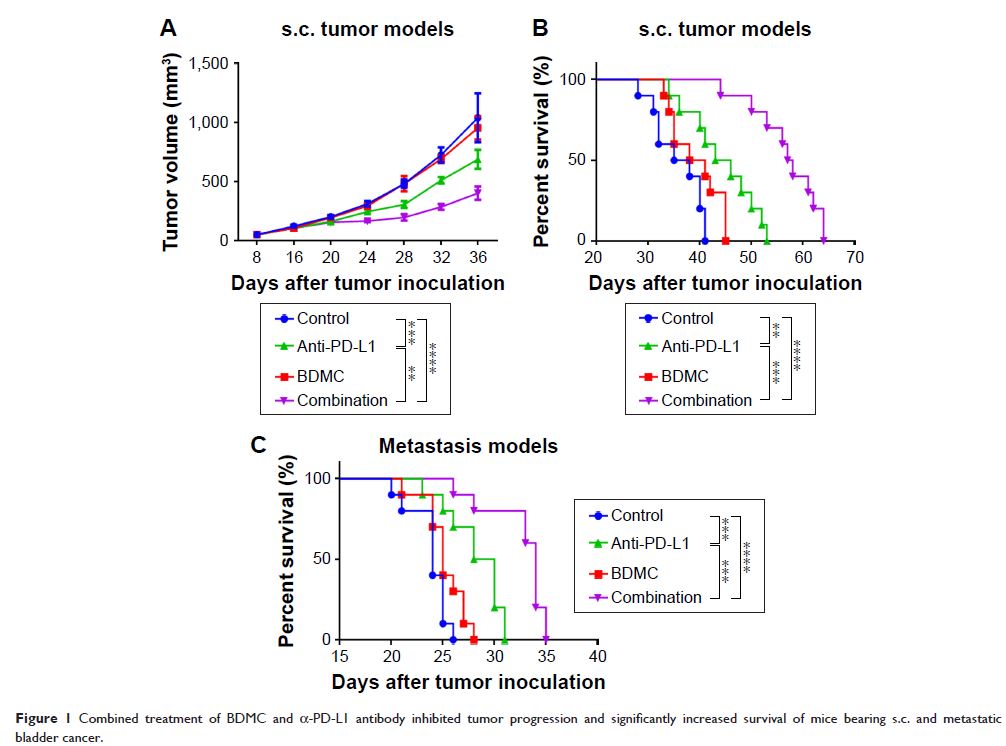
As a result, this combination treatment strategy significantly prolonged
survival of intraperitoneal metastasized bladder cancer bearing mice,
suggesting that bisdemethoxycurcumin in combination with α-PD-L1 antibody may
be promising for bladder cancer patients.
Keywords: bladder
cancer, immunotherapy, bisdemethoxycurcumin, PD-L1, combination therapy,
metastasis