103855
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

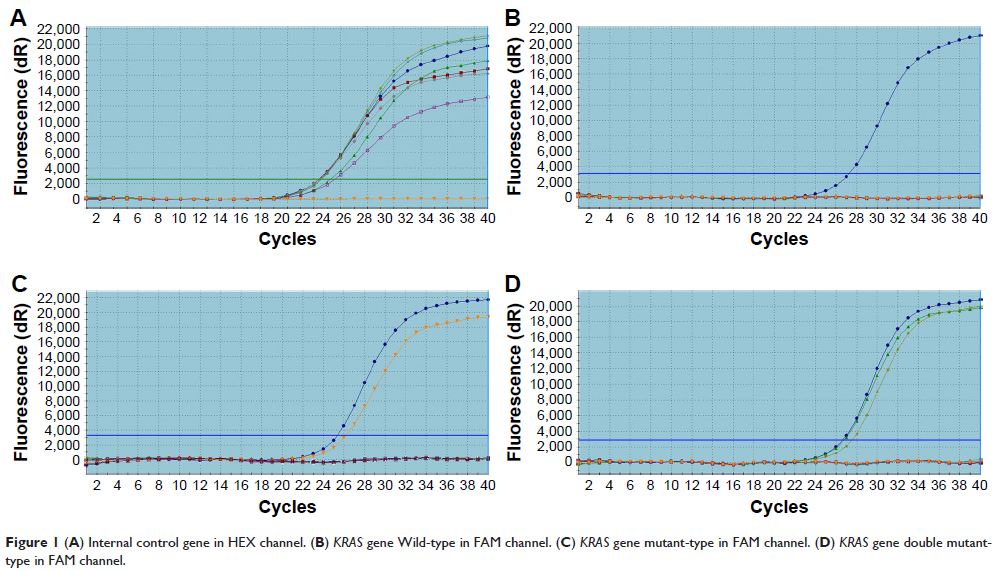
原发性与配对转移结肠直肠癌及 KRAS 突变患者的临床病理特征与存活率之间的关系
Authors Pang X, Li Q, Ma Z, Shi Y, Ma Y, Li X, Cui W, Zhang W
Received 25 January 2017
Accepted for publication 31 March 2017
Published 19 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2645—2654
DOI http://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S133203
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Federico Perche
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Abstract: The KRAS gene mutation is involved in several
types of tumors. However, the potential role of the KRAS mutation in human primary and paired
metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) among different nationalities is poorly
understood. In the present study, we assessed the relationship between KRAS mutation status and overall survival
(OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in 230 patients with primary and paired
metastatic CRC. The KRAS mutation rate in primary CRC tissue
was 43.0% (99/230), which was higher than in paired metastatic CRC, which was
31.9% (23/72; P <0.001).
Clinicopathologically, the KRAS gene
mutation rate was higher in tumors that had infiltrated more deeply (T3, T4)
and in lymph node (LN) metastases (N1/N2) (P =0.029 and P =0.010, respectively). The KRAS gene status
did not differ between the Han and Uyghur nationalities in both primary and
metastatic CRC. In 72 paired cases, the KRAS mutation rate in primary CRC was
significantly higher than in metastatic CRC (P <0.001) and in
metastatic CRC that had infiltrated more deeply (T3, T4) (P =0.034). In the metastatic cases,
the KRAS gene mutation rate was higher in
patients aged over 65 years (P =0.035).
Specifically, KRAS mutation was correlated with a poorer
OS and DFS (P =0.004 and P =0.029,
respectively). In our study, 35 patients with wild-type KRAS who received cetuximab targeted
therapy had a better DFS than patients with mutant KRAS (P =0.029). The
results of the current study demonstrate that the KRAS status is significantly associated
with infiltrating LN metastases and the TNM stage in primary CRC. In addition,
the results show that the KRAS mutation is significantly more common
in primary tumors than in paired metastatic CRC, and the KRAS mutation is correlated with a shorter
OS and DFS, as patients with wild-type KRAS who received cetuximab experienced a
longer DFS.
Keywords: CRC, KRAS , primary,
metastatic, cetuximab, survival