102494
论文已发表
提 交 论 文
注册即可获取Ebpay生命的最新动态
注 册
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

在中国农村高血压患者中利用以家庭成员为基础的监督管理
Authors Huang S, Chen Y, Zhou J, Wang J
Published Date July 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 1035—1042
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S66777
Received 24 April 2014, Accepted 5 June 2014, Published 31 July 2014
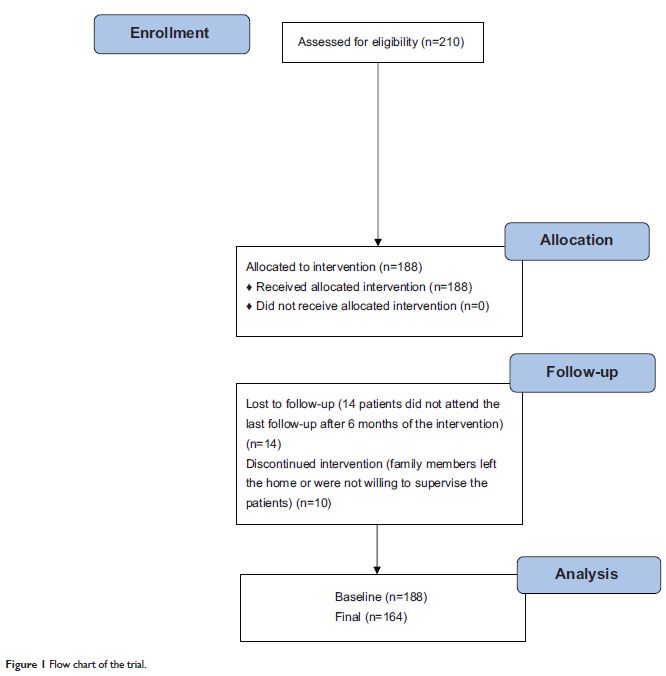
Abstract: Medication nonadherence is a major problem in the management of hypertension. The aim of this study was to develop a family member-based supportive therapy for patients with hypertension to provide an affordable way to access essential health services and to ensure adequate control of blood pressure. This study applied a mixed methods approach using qualitative and quantitative study designs in Yangzhong County, a rural area in the People's Republic of China. Findings from indepth interviews demonstrated that the limited effects of traditional health education, a lack of professional advice regarding antihypertensive treatment, and age were related to a patient's adherence with regular blood pressure measurement and taking medication. We also performed a quantitative study, selecting two villages in Yangzhong County as study sites. A total of 188 patients with hypertension were invited to participate in a 6-month family member-based intervention trial. The primary outcomes were the acceptability and feasibility of the intervention strategy. Secondary outcomes included medication adherence and changes in blood pressure. More than 75% of patients expressed a wish for external reminders, and 93.5% responded that they would accept the family member-based supervision. The patients preferred their spouse or a child as the supervisor. After the 6-month intervention, the proportion of patients with uncontrolled blood pressure decreased from 87.2% to 45.7%. This pilot study shows that external supervision by family members is acceptable and feasible for patients with hypertension; it also shows favorable effects with regard to improved treatment adherence and blood pressure control. Future randomized controlled trials with modified intervention measures are needed to validate this finding.
Keywords: hypertension, treatment, adherence, supervision, intervention